ELCB Full Form | ELCB Working Principle | What is ELCB | ELCB Full Form in Electrical | What is ELCB in Electrical | RCCB Vs ELCB
In today's electrical systems, safety is paramount, and one of the most important safety devices is the Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB). It plays a crucial role in preventing electric shock hazards and protecting electrical installations from potential damage caused by ground faults. In this detailed blog post, we'll dive deep into what an ELCB is, its types, working principles, and why it is an indispensable part of modern electrical safety systems
What is an Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)?
An Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical systems to detect and interrupt leakage currents that flow to the earth (ground). These currents, if left unchecked, can cause electric shocks to humans or lead to fire hazards due to electrical leakage. The ELCB helps protect both people and equipment by breaking the circuit whenever it detects unsafe levels of current leaking to the ground.
Types of ELCB: Voltage ELCB vs. Current ELCB
There are two primary types of ELCBs, each based on different working principles:
Voltage Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (Voltage-ELCB):
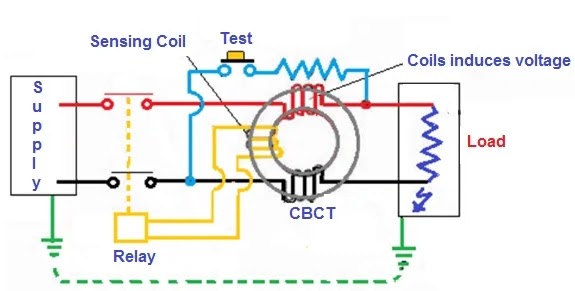
- Working Principle: This type of ELCB operates by monitoring the voltage between the electrical equipment and the earth (ground). If the voltage exceeds a certain threshold, it indicates a potential leakage current, and the ELCB will disconnect the power supply.
- Components: A sensing coil, trip relay, and main contacts are the key components of a voltage ELCB.
- Advantages: It’s simple in design and was historically one of the first devices used to detect earth faults.
- Disadvantages: It requires a separate earth connection and can be less sensitive than current-based systems. Its use is now considered outdated in many countries.
Current Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (Current-ELCB or RCCB – Residual Current Circuit Breaker):
- Working Principle: This type of ELCB measures the imbalance in current between the live (phase) and neutral wires. In a healthy system, the current in both should be equal. If there’s an imbalance (which indicates current leaking to earth), the device trips, disconnecting the circuit.
- Components: It includes a differential current transformer (to sense imbalances), a relay mechanism, and contacts that open to interrupt the circuit.
- Advantages: Highly sensitive to even small leakage currents (typically as low as 30mA), making it more effective at protecting against electric shock.
- Disadvantages: More complex than voltage-ELCBs and can be more expensive.
How Does an ELCB Work?
The core function of an ELCB revolves around detecting leakage currents and interrupting the circuit to prevent potential hazards. Let’s walk through the basic operational flow:
Detection of Leakage: In a normal situation, the current flowing through the phase and neutral wires is equal. If a person comes in contact with a live wire or there’s a fault in the equipment, some current leaks to the ground.
Sensing Imbalance: A current-ELCB monitors this imbalance using a current transformer (CT) to detect differences between the phase and neutral wires. If the imbalance exceeds a predefined safe value (typically 30mA), the device recognizes it as an earth fault.
Trip Mechanism: Upon detecting a leakage, the ELCB triggers its trip mechanism, opening the contacts and cutting off the power supply to the circuit. This prevents further leakage and eliminates the risk of shock or fire.
Manual Reset: Once tripped, the ELCB must be manually reset by an operator. This ensures that the fault is addressed before the circuit can be re-energized.
Compatibility: Modern ELCBs can be integrated with various types of circuit breakers (MCBs, MCCBs) for combined protection against overload, short circuit, and earth leakage.
Advantages of Using ELCBs
Protection Against Electric Shock: ELCBs are essential in preventing electric shock by cutting off the power supply whenever leakage current is detected.
Fire Prevention: Earth faults and leakage currents can lead to overheating and fire hazards. ELCBs help prevent these risks by interrupting the circuit early.
Equipment Protection: Sensitive electrical equipment can be damaged by leakage currents. ELCBs help protect your investments by keeping leakage in check.
Compliance with Safety Regulations: Many regions have electrical safety standards and codes that mandate the use of ELCBs or similar protective devices in homes and commercial buildings.
Limitations of ELCBs
Not Effective for All Faults: ELCBs are designed to detect earth leakage, but they may not provide adequate protection against overloads or short circuits. They need to be used in conjunction with other protective devices like MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers).
False Tripping: In some cases, ELCBs may trip due to harmless leakage currents (e.g., from certain appliances or environmental conditions), leading to unnecessary power outages.
Maintenance: Over time, ELCBs require maintenance to ensure that they remain sensitive and responsive to faults. Dust or mechanical wear can affect their performance.
Applications of ELCB
ELCBs are commonly used in electrical installations to protect against electrical shock and electrical fires caused by ground faults. They are used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. ELCBs are commonly used in the following applications:
- Lighting circuits
- Power circuits
- Motors
- Transformers
- Welding machines
- Battery chargers
- Medical equipment
- Electronic equipment
Popular Makes and Ratings of ELCB
There are several popular makes and ratings of ELCB available in the market. Following are some of the popular ELCB brands and their ratings:
Schneider Electric: Schneider Electric offers a wide range of ELCBs with various ratings ranging from 25A to 100A. They also offer ELCBs with a voltage rating of 240V and 415V.
Legrand: Legrand offers ELCBs with a current rating of 16A, 25A, 40A, and 63A. They also offer ELCBs with a voltage rating of 240V and 415V.
Hager: Hager offers ELCBs with a current rating of 25A, 40A, 63A, and 100A. They also offer ELCBs with a voltage rating of 240V and 415V.
ABB: ABB offers ELCBs with a current rating of 16A, 25A, 40A, 63A, and 100A. They also offer ELCBs with a voltage rating of 240V and 415V.
Siemens: Siemens offers ELCBs with a current rating of 25A, 40A, 63A, and 100A. They also offer ELCBs with a voltage rating of 240V and 415V.
L&T: L&T offers ELCBs with a current rating of 25A, 40A, 63A, and 100A. They also offer ELCBs with a voltage rating of 240V and 415V.
RCCB Vs ELCB
Functionality: RCCB is designed to protect against residual current faults caused by insulation failure, whereas ELCB is designed to protect against earth leakage faults caused by an imbalance in the phase and neutral conductors.
Operation: RCCB trips when the current flowing through the circuit differs from the current returning from the circuit, whereas ELCB trips when the current flowing through the phase conductor does not return through the neutral conductor.
Application: RCCB is commonly used in residential and commercial buildings, whereas ELCB is commonly used in industrial and high-voltage applications.
Conclusion
ELCB is an essential safety device used in electrical installations to protect against electrical shock and electrical fires caused by ground faults. It detects any current leakage in the electrical circuit and trips the circuit breaker to stop the current flow. There are two types of ELCBs: voltage-operated ELCB and current-operated ELCB. ELCBs are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
FAQs
What is the function of an ELCB?
An ELCB functions as a safety device in electrical installations to detect and prevent electrical shock caused by a ground fault. It detects any current leakage in the electrical circuit and trips the circuit breaker to stop the current flow.
How does an ELCB work?
An ELCB works by detecting any current leakage in the electrical circuit. It consists of a sensing coil and a tripping mechanism. The sensing coil is connected in series with the electrical circuit, and when there is an earth fault, the current flows through the sensing coil. This causes a magnetic field to be generated, which activates the tripping mechanism and opens the circuit breaker, stopping the current flow.
What are the types of ELCB?
There are two types of ELCBs: Voltage operated ELCB and Current operated ELCB. Voltage operated ELCB works on the principle of voltage sensing, while current operated ELCB works on the principle of current sensing.
What are the applications of ELCB?
ELCBs are commonly used in electrical installations to protect against electrical shock and electrical fires caused by ground faults. They are used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications for lighting circuits, power circuits, motors, transformers, welding machines, battery chargers, medical equipment, and electronic equipment.
What are the popular makes of ELCB?
Some of the popular ELCB brands in the market include Schneider Electric, Legrand, Hager, ABB, Siemens, and L&T.
How to select the appropriate ELCB rating?
The selection of the appropriate ELCB rating depends on factors such as the maximum current flow, the voltage rating, and the type of load that the circuit is carrying. It is recommended to consult with a licensed electrician before selecting and installing an ELCB.






Post a Comment