What is 6 pulse drive | 12 pulse drive | 18 pulse drive
A 6-pulse drive refers to a type of variable frequency drive (VFD) that uses a six-pulse rectifier to convert AC power to DC power, which is then converted back to AC power with a pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter to control the speed of an AC motor.
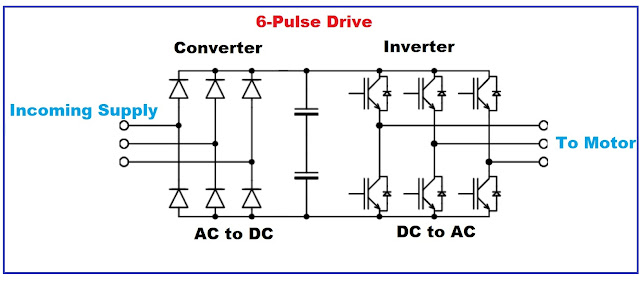
6-Pulse Drive
The six-pulse rectifier consists of six diodes that rectify the incoming AC power, resulting in a DC voltage with a pulsating waveform. This pulsating DC voltage is then smoothed out by a capacitor bank to provide a more constant DC voltage for the PWM inverter.
The PWM inverter uses switches to rapidly turn the DC voltage on and off, creating a series of pulses that simulate an AC waveform. By adjusting the frequency and duration of these pulses, the inverter can control the speed and torque of the connected AC motor.
While a 6-pulse drive is a relatively simple and cost-effective VFD solution, it can produce harmonic distortion in the AC power supply due to the pulsating DC waveform. This can cause interference with other electrical equipment and result in increased energy consumption and wear on the motor. To mitigate these issues, more advanced VFDs may use 12-pulse or 18-pulse rectifiers or active front-end (AFE) technology.
12-Pulse Drive
A 12-pulse drive is a type of variable frequency drive (VFD) that uses a 12-pulse rectifier to convert AC power to DC power before being converted back to AC power by a pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter. The 12-pulse rectifier is made up of two six-pulse rectifiers that are connected in series with a phase shift transformer between them.
The phase shift transformer is designed to introduce a phase shift of 30 degrees between the two six-pulse rectifiers, which helps to reduce the harmonic distortion in the AC power supply. By reducing harmonic distortion, a 12-pulse drive can improve the efficiency of the motor and reduce wear and tear on both the motor and other electrical equipment in the system.
A 12-pulse drive is typically used in larger applications where harmonic distortion is a concern, such as in high-power motors and other heavy-duty industrial equipment. Compared to a 6-pulse drive, a 12-pulse drive is more complex and typically more expensive to implement, but it can provide improved performance and reliability in certain applications.
18-Pulse Drive
An 18-pulse drive is a type of variable frequency drive (VFD) that uses an 18-pulse rectifier to convert AC power to DC power before being converted back to AC power by a pulse width modulation (PWM) inverter. The 18-pulse rectifier is made up of three six-pulse rectifiers that are connected in series with two phase shift transformers between them.
The phase shift transformers are designed to introduce a phase shift of 20 degrees between the three six-pulse rectifiers, which helps to reduce the harmonic distortion in the AC power supply even further than a 12-pulse drive. By reducing harmonic distortion, an 18-pulse drive can improve the efficiency of the motor and reduce wear and tear on both the motor and other electrical equipment in the system.
An 18-pulse drive is typically used in larger applications where harmonic distortion is a major concern, such as in high-power motors and other heavy-duty industrial equipment. Compared to a 12-pulse drive, an 18-pulse drive is even more complex and typically more expensive to implement, but it can provide improved performance and reliability in certain applications where harmonic distortion is critical.
Frequently Asked Questions about 6-pulse drives:
What is a 6-pulse drive used for?
A 6-pulse drive is used to control the speed of AC motors, typically in industrial applications. They are commonly used in fans, pumps, conveyors, and other types of machinery.
How does a 6-pulse drive work?
A 6-pulse drive converts AC power into DC power using six diodes, which are arranged in a three-phase bridge configuration. The DC power is then converted back into AC power using a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique that controls the speed of the motor.
What are the advantages of a 6-pulse drive?
The advantages of a 6-pulse drive include lower cost, simpler design, and higher efficiency compared to other types of motor drives. They are also capable of controlling the speed and torque of the motor with high accuracy.
What are the disadvantages of a 6-pulse drive?
The disadvantages of a 6-pulse drive include harmonic distortion, which can cause interference with other electronic equipment and reduce the efficiency of the drive. They also produce torque pulsations, which can cause vibrations and noise in the motor.
How do you reduce harmonic distortion in a 6-pulse drive?
Harmonic distortion can be reduced in a 6-pulse drive by adding harmonic filters or using a higher-pulse drive, such as a 12-pulse or 18-pulse drive. These drives use more diodes and are more complex, but they produce less harmonic distortion.
What are the maintenance requirements for a 6-pulse drive?
The maintenance requirements for a 6-pulse drive
include checking and replacing the diodes as needed, monitoring the cooling
system, and cleaning the drive to prevent dust and dirt buildup. It is also
important to regularly check and calibrate the drive's speed and torque control
settings.
Frequently Asked Questions about 12-pulse drives:
What is a 12-pulse drive used for?
A 12-pulse drive is used to control the speed of AC motors, typically in industrial applications. They are commonly used in fans, pumps, conveyors, and other types of machinery.
How does a 12-pulse drive work?
A 12-pulse drive converts AC power into DC power using two six-pulse bridges that are connected in a series. The two bridges are supplied with a phase shift of 30 degrees, which creates a smoother DC output voltage. The DC power is then converted back into AC power using a pulse-width modulation (PWM) technique that controls the speed of the motor.
What are the advantages of a 12-pulse drive?
The advantages of a 12-pulse drive include reduced harmonic distortion compared to a 6-pulse drive. The use of two bridges and a phase shift of 30 degrees creates a smoother DC output voltage, which reduces harmonic distortion and interference with other electronic equipment.
What are the disadvantages of a 12-pulse drive?
The disadvantages of a 12-pulse drive include higher cost and more complex design compared to a 6-pulse drive. They also produce torque pulsations, which can cause vibrations and noise in the motor.
How do you reduce harmonic distortion in a 12-pulse drive?
Harmonic distortion can be reduced in a 12-pulse drive by using a higher-pulse drive, such as an 18-pulse or 24-pulse drive. These drives use more bridges and are more complex, but they produce less harmonic distortion.
What are the maintenance requirements for a 12-pulse drive?
The maintenance requirements for a 12-pulse
drive are similar to those of a 6-pulse drive and include checking and
replacing the diodes as needed, monitoring the cooling system, and cleaning the
drive to prevent dust and dirt buildup. It is also important to regularly check
and calibrate the drive's speed and torque control settings.






Post a Comment