Field Oriented Control of Induction Motor | Field Oriented Control | Vector Control of Induction Motor
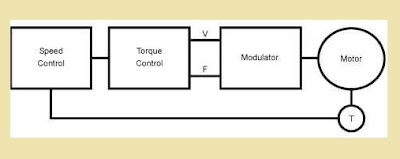
Vector control of Induction Motor is also known as field-oriented control (FOC), is a method of controlling the speed and torque of an electric motor with high precision and efficiency. It is used in variable frequency drives (VFDs) and other motor control applications. Field Oriented Control (FOC) is a method of controlling the speed and torque of an induction motor by controlling the magnetic field generated by the stator windings.
FOC is a popular control technique used in modern variable speed drives, and it is particularly well-suited for applications that require high precision and dynamic performance. In traditional induction motor control, the voltage and frequency of the power supplied to the motor are adjusted to control its speed and torque. However, this method can result in poor dynamic response and low efficiency at low speeds. FOC addresses these issues by controlling the magnetic field of the motor directly, rather than relying on changes to the input voltage and frequency.
In FOC, the current flowing through the stator windings is separated into two components: a direct current (DC) component that generates the magnetic field in the rotor, and a quadrature current (QC) component that generates the torque in the motor. By controlling these two components independently, the speed and torque of the motor can be precisely controlled.
One of the key advantages of FOC is its ability to provide high torque at low speeds. This is particularly important in applications such as robotics, where high precision and responsiveness are critical. FOC also provides improved efficiency and reduced losses compared to traditional induction motor control methods.
To implement FOC, a controller is typically used to calculate the DC and QC components of the stator current based on feedback from sensors such as encoders or tachometers. The controller then adjusts the current supplied to the stator windings to achieve the desired speed and torque.
FOC is widely used in industrial and commercial applications, including manufacturing, transportation, and renewable energy. It is a powerful tool for improving the performance, efficiency, and reliability of induction motor systems, and it is likely to remain an important area of research and development in the years to come.
However, vector control requires more complex algorithms and processing power than simpler control methods, which can make it more expensive and complex to implement. It also requires accurate sensor feedback and calibration to achieve optimal performance.
A vector motor is a type of electric motor that is designed to work with vector control or field-oriented control (FOC) techniques. Vector control is a method of controlling the speed and torque of an electric motor with high precision and efficiency, and it requires specific motor characteristics to work effectively.
A vector motor is typically a three-phase induction motor with additional features such as high-precision encoders, temperature sensors, and special windings. These features allow for more accurate measurement and control of the motor's speed, torque, and position, which are critical for vector control.
Vector motors are capable of operating at high torque and low speeds with high efficiency, which makes them ideal for applications such as servo systems, robotics, and machine tools. They are also used in variable frequency drives (VFDs) for precise control of motor speed and torque.
Conclusion
Vector motors are more complex and expensive than standard induction motors, but they offer superior performance and efficiency in many applications. They can be used in both open-loop and closed-loop control systems, depending on the requirements of the application.






Post a Comment