Energy Efficient Motors | Advantages Of Energy Efficient Motors | Less Air Gap In Energy Efficient Motors Increase
Energy efficient motors are becoming increasingly popular as individuals and businesses look for ways to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on energy bills. These motors are designed to use less electricity than traditional motors, while still delivering the same level of performance. By using high-quality materials, advanced designs, and innovative features such as variable frequency drives, energy efficient motors can save a significant amount of energy and money over their lifetime. In this article, we will explore the benefits of energy efficient motors, the different types available, and how to select the right motor for your application.
Energy Efficient Motors | Advantages Of Energy Efficient Motors
- Energy efficient motors are designed to use less electricity than standard motors, making them more environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
- These motors are typically more efficient due to their design, which includes features such as higher-quality materials, improved windings, and reduced friction.
- Energy efficient motors can save a significant amount of energy and money over their lifetime, making them a smart investment for any business or individual.
- There are various types of energy efficient motors, including permanent magnet motors, synchronous reluctance motors, and induction motors with variable frequency drives.
- Energy efficient motors are available in a range of sizes and power ratings, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- When selecting an energy efficient motor, it is important to consider factors such as load requirements, operating conditions, and the motor's efficiency rating.
Main Objectives of energy-efficient motors are:
Energy Savings: The primary objective of energy-efficient motors is to reduce energy consumption and save energy. Energy-efficient motors use advanced technologies and materials to reduce energy losses and improve efficiency. These motors consume less electricity than standard motors, which means they can help to lower energy bills and reduce energy waste.
Environmental Benefits: The use of energy-efficient motors can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other harmful pollutants. By reducing energy consumption, energy-efficient motors can help to reduce the carbon footprint of businesses and industries, and contribute to the global effort to mitigate climate change.
Cost Savings: Energy-efficient motors can help businesses and industries to save money by reducing operating costs. Although energy-efficient motors may have a higher initial cost than standard motors, their lower energy consumption means that they can pay for themselves in energy savings over time. Additionally, energy-efficient motors may require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan, which can also result in cost savings.
Improved Performance: Energy-efficient motors are designed to operate more efficiently and reliably than standard motors. They can provide better performance, higher torque, and more precise control, which can improve the productivity and quality of industrial processes.
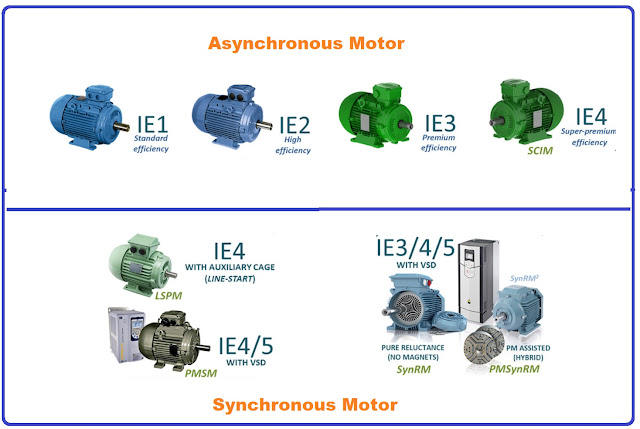
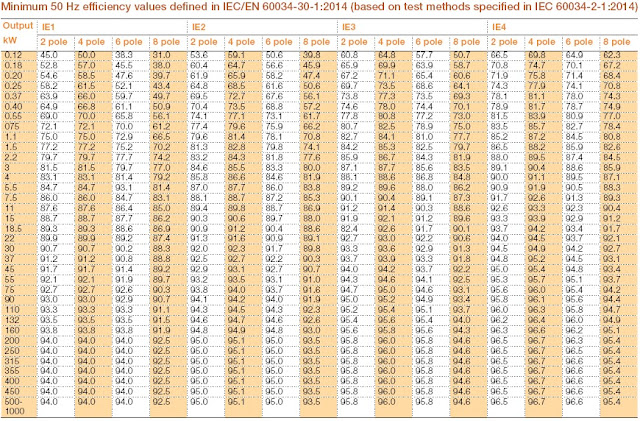
IEC/EN 60034-30-1 Standard
This IEC standard is concerned with the global harmonization of energy efficiency classes for electric motors. Compared with IEC/EN 60034-30: 2008, it significantly expands the range of products covered with the inclusion of 8-pole motors and introduces IE4 efficiency performance class for electric motors.
All technical constructions of motors are covered as long as they are rated for direct on-line operation. Whereas the previous edition covered only three-phase products, the new standard also includes single-phase motors, as well as line-start permanent magnet motors.
IE1-Standard efficiency
IE2-High efficiency
IE3 -Premium efficiency
IE4 –Super Premium efficiency
Classification
IE1: Standard Efficiency motors have an efficiency rating that falls below the minimum requirements set by the IEC. These motors are typically used in applications where energy efficiency is not a major concern.
IE2: High Efficiency motors have an efficiency rating that meets or exceeds the minimum requirements set by the IEC. These motors are up to 6% more efficient than standard efficiency motors and can provide significant energy savings.
IE3: Premium Efficiency motors have an efficiency rating that exceeds the minimum requirements set by the IEC. These motors are up to 13% more efficient than standard efficiency motors and up to 3% more efficient than high-efficiency motors. They are suitable for a wide range of applications and are commonly used in industrial and commercial settings.
IE4: Super Premium Efficiency motors have the highest efficiency rating and exceed the minimum requirements set by the IEC. These motors are up to 35% more efficient than standard efficiency motors and up to 15% more efficient than premium efficiency motors. They are typically used in high-demand applications where energy efficiency is a top priority, such as large industrial facilities or data centers.
Key Construction Features of IE Motors
IE (International Efficiency) motors are typically constructed in a similar manner to other electric motors, but they incorporate design features and materials that improve their energy efficiency.
1. Rotor design: IE motors typically have a squirrel-cage rotor design, which is more efficient than other types of rotor designs.
2. Stator design: The stator of an IE motor is designed to minimize energy losses due to eddy currents and hysteresis losses.
3. Lamination materials: High-grade lamination materials are used in the construction of IE motors to minimize energy losses due to magnetic hysteresis and eddy currents.
4. Windings: The windings in an IE motor are typically made of high-quality copper wire, which has lower resistance and therefore lower energy losses.
5. Bearings: High-quality bearings are used in the construction of IE motors to minimize friction losses.
6. Fan design: The fan used to cool an IE motor is designed to reduce air resistance and minimize energy losses.
In addition to these construction features, IE motors may also incorporate other technologies such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), which can further improve their energy efficiency. Overall, the construction of IE motors is focused on reducing energy losses and improving overall efficiency, which can provide significant energy savings over the lifetime of the motor.
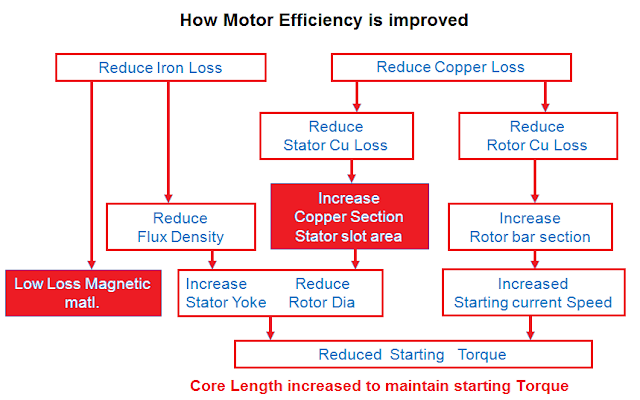
Ways by which losses are minimized in IE motors:
IE (International Efficiency) motors are designed to minimize energy losses through a variety of design features and materials.
1. Core losses: Core losses occur due to the hysteresis and eddy currents that are generated in the motor's magnetic core. To minimize core losses, IE motors use high-quality laminations made from low-loss magnetic steel. These laminations are stacked together to form the core, with insulation between each layer to reduce eddy current losses.
2. Copper losses: Copper losses occur due to the resistance of the copper windings in the motor. To minimize copper losses, IE motors use high-quality copper wire with low resistance. The wire is also carefully sized to minimize losses and ensure optimal performance.
3. Mechanical losses: Mechanical losses occur due to friction and windage in the motor. To minimize these losses, IE motors use high-quality bearings and a carefully designed fan system to reduce air resistance and ensure smooth operation.
4. Efficiency of the rotor: IE motors are typically designed with a squirrel-cage rotor, which is more efficient than other rotor designs. The rotor bars are carefully sized and spaced to minimize losses and ensure optimal performance.
5. Efficient motor control: The use of efficient motor control strategies, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), can also help to minimize losses in IE motors. VFDs can be used to adjust the speed of the motor based on the required load, which can result in significant energy savings.
By incorporating these design features and materials, IE motors are able to minimize energy losses and operate at high levels of efficiency. This can result in significant energy savings and lower operating costs over the lifetime of the motor.
IE Motors Applications
IE1 motors are the least efficient and are typically used in low-demand applications where energy efficiency is not a major concern. They are commonly found in small machines and appliances, such as fans, pumps, and conveyors.
IE2 motors are more efficient than IE1 motors and are typically used in applications where energy efficiency is important but not critical. They are commonly found in larger machines and equipment, such as compressors, pumps, and industrial fans.
IE3 motors are even more efficient than IE2 motors and are typically used in applications where energy efficiency is critical. They are commonly found in high-demand applications, such as air conditioning systems, large pumps, and compressors.
IE4 motors are the most efficient and are used in applications where energy efficiency is of utmost importance, such as in high-speed machinery or applications with continuous duty cycles.
Motors covered under this standard
The new standard covers a wider scope of products.
The power range has been expanded to cover motors from 120 W to 1000 kW.
All technical constructions of electric motors are covered as long as they are rated for direct on-line operation.
The coverage of the new standard includes:
- Single speed electric motors (single and three phase),50 and 60 Hz
- 2, 4, 6 or 8 poles
- Rated output PN from 0.12 kW to 1000 kW
- Rated voltage UN above 50 V up to 1 kV
- Motors, capable of continuous operation at their rated power with a temperature rise within the specified insulation temperature class
- Motors, marked with any ambient temperature within the range of -20 °C to +60 °C
- Motors, marked with an altitude up to 4000 m above sea level
Motors excluded by this standard
- Single-speed motors with 10 or more poles or multi-speed motors
- Motors completely integrated into a machine (for example, pump, fan or compressor) that cannot be tested separately from the machine.
- Brake motors, when the brake cannot be dismantled or separately fed.
Energy Efficient motor more expensive because
- These motors are generally priced 5 - 15 % higher
- More laminations - longer core length and/or
- High Grade (low loss) laminations
- More Copper in winding
Motor Efficiency improvement Steps
Less Air Gap In Energy Efficient Motors Increase
Less air gap in energy-efficient motors does not necessarily increase efficiency, but it can have a positive impact on the motor's efficiency under certain conditions.
An air gap is the space between the rotor and the stator in an electric motor. The larger the air gap, the more energy is required to turn the motor because the magnetic field has to work harder to bridge the gap. Therefore, reducing the air gap can potentially increase the motor's efficiency by reducing the amount of energy required to produce the same amount of torque.
However, reducing the air gap too much can also cause problems. If the air gap is too small, the rotor can make contact with the stator, causing damage to the motor. Additionally, reducing the air gap can increase the motor's susceptibility to overheating, which can reduce its lifespan.
Therefore, while reducing the air gap can increase efficiency under certain conditions, it is important to balance this with other factors such as motor reliability and durability. Ultimately, the best air gap for a given motor will depend on a variety of factors, including the motor's design, operating conditions, and intended use






Post a Comment