Cable Schedule | Cable Schedule Format | Cable Schedule Electrical | Junction Box Schedule
Are you struggling to streamline your electrical engineering projects? A Cable Schedule might be the key to enhancing efficiency and organization in your installations. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the essence of cable scheduling, exploring its significance, techniques, and best practices that can lead to project success. By the end, you’ll be equipped with valuable insights that ensure optimal management of your electrical systems.
What is a Cable Schedule?
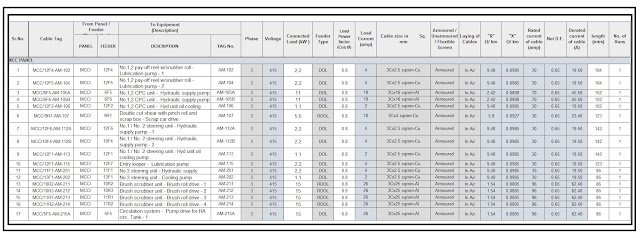
A cable schedule serves as a vital document that details every cable used in an electrical project. It typically includes:
- Cable Type: Such as XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene) or PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride).
- Number of Cores: The conductors within the cable (e.g., 3-core, 4-core).
- Cable Size: Measured in mm² (square millimeters) or AWG (American Wire Gauge).
- Length of the Cable: Total measurement in meters or feet.
- Starting and Termination Points: Locations where the cable begins and ends.
- Voltage Level: Categories like low, medium, or high voltage.
- Installation Method: Such as conduits, trenches, or direct burial.
- Cable Route Identification: A clear path for installation.
- Relevant Remarks: Any special conditions like fire resistance or waterproofing.
This document is crucial during the design phase and acts as a reference throughout installation, commissioning, and future maintenance.
Importance of Cable Scheduling
1. Organization and Efficiency A well-prepared cable schedule provides clear information, aiding electricians and engineers in efficient planning and reducing installation errors.
2. Cost Control Accurate cable schedules minimize waste by ensuring correct procurement, leading to better labor and equipment planning.
3. Safety Compliance Cable schedules ensure adherence to safety standards, maintaining compliance with regulations like the NEC (National Electrical Code) or IEC standards.
4. Ease of Maintenance and Modifications A comprehensive schedule simplifies future maintenance and modifications, allowing technicians to locate cables with ease.
5. Improved Communication A shared cable schedule fosters collaboration among stakeholders—contractors, engineers, and project managers—reducing misunderstandings.
Cable Schedule Format
Components of a Cable Schedule
A cable schedule serves as a vital document that details every cable used in an electrical project. It typically includes:
This document is crucial during the design phase and acts as a reference throughout installation, commissioning, and future maintenance.
How to Create a Cable Schedule
Creating an effective cable schedule involves the following steps:
1. Understand the System Layout Begin with a thorough understanding of the electrical layout by studying the Single Line Diagram (SLD).
2. Cable Sizing Calculations Perform detailed calculations for current-carrying capacity, voltage drop, and short-circuit ratings to determine the correct cable sizes.
3. Cable Length Estimation Estimate lengths considering site layout and potential obstacles. Include a contingency for future flexibility.
4. Assign Cable IDs Create unique identifiers for each cable using a logical naming convention (e.g., MCB01-DB02-XLPE).
5. Determine the Installation Method Select the installation method based on project requirements, considering factors such as protection and insulation.
6. Record Special Requirements Document any special conditions like fire-resistant cables or waterproofing that may impact installation.
7. Final Documentation Compile all information into a structured table using software like Excel or AutoCAD, ensuring easy reference.
Required data or information for Cable schedule preparation:
- Basic Engineering Design Data
- I&C Design Basis
- P&ID diagram
- Instrument Index and Instrument I/O List
Cable Scheduling Best Practices
- Use a Standardized Format: Ensures clarity across teams.
- Cross-Check with SLDs: Verify all cables are accounted for and correctly sized.
- Regular Updates: Keep the cable schedule dynamic to reflect design changes.
- Incorporate Software Tools: Leverage electrical design software like ETAP or AutoCAD for efficiency.
- Account for Environmental Factors: Consider ambient temperature and other conditions that may affect cable performance.
- Plan for Future Expansion: Design with flexibility in mind to accommodate future needs.
Common Mistakes in Cable Scheduling and How to Avoid Them
- Incorrect Cable Sizing: Always perform thorough calculations to avoid project delays.
- Inadequate Documentation: Ensure all installation details are well-documented.
- Lack of Coordination: Foster collaboration among electrical, mechanical, and civil teams.
Cable Schedule Software Tools
ETAP: Advanced design tool for load flow and short-circuit analysis, featuring a cable scheduling module.
AutoCAD Electrical: Helps generate wiring and cable schedules as part of the electrical layout.
Cable Scheduler: Offers dedicated tools for cable scheduling and routing diagrams.
Junction Box Schedule
A junction box schedule is a document that lists all the junction boxes and their associated details in a construction or electrical installation project. The purpose of a junction box schedule is to ensure that all junction boxes are accounted for and that they are installed correctly and in accordance with the project specifications
.A typical junction box schedule may include the following information:
- Junction box number or identifier
- Junction box location or installation location
- Junction box type or size
- Junction box rating or capacity
- Number of conductors or cables connected to the junction box
- Conductor or cable size
- Conductor or cable type or insulation rating
- Junction box manufacturer and model number
- Wiring diagram or schematic showing the connections to the junction box
Example of a Junction Box Schedule for an electrical installation project:
The remaining columns provide information about the number and size of conductors or cables connected to the junction box, the conductor type or insulation rating, and the manufacturer and model number of the junction box. The last column shows the wiring diagram or schematic that depicts the connections to the junction box.
Conclusion
Cable scheduling is crucial for the successful installation of electrical systems, ensuring safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulatory standards. By following a systematic approach and adopting best practices, engineers can enhance project organization and communication, avoiding costly errors and delays.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do I prepare my cable schedule for substation?
To prepare a cable schedule for a substation, you will need to gather information about the equipment and cables being used, as well as the power requirements and load demands.
Include the following information for each cable:
Cable Number - a unique identifier for each cable in the system.
Cable Type / Specification - the type and specification of the cable being used, such as XLPE insulated, copper conductor, armored cable, etc.
Cable Size - the diameter or cross-sectional area of the cable, typically measured in millimeters or square millimeters.
Cable Length - the length of the cable, measured in meters or kilometers.
Source and destination termination description - the description of the equipment or device where the cable originates and terminates, including any necessary details such as voltage rating or phase.
Cable gland type and size for each incoming cable - the type and size of the cable gland used for each incoming cable, including any necessary details such as thread size or material.
What is cable drum schedule?
A cable drum schedule is a document that provides details about the cable drums that will be used for a particular project or installation. It typically includes information such as the type and size of cable, the length of the cable, the diameter of the drum, the weight of the drum, and any special handling requirements or instructions. cable drum schedule include information on how the cable will be cut and used for construction purposes. This information can be important for ensuring that the cable is used efficiently and that there is minimal waste. The schedule may indicate how many sections the cable will be cut into, what lengths each section will be, and where each section will be used in the construction project.
What is junction box schedule?
A junction box schedule is a document or a table that lists all the junction boxes installed in a building or a construction project. The schedule typically includes the location of each junction box, its size, the number of conductors, and other relevant information such as the type of cover or lid used to secure the junction box.
Junction box schedules are commonly used in electrical engineering and construction projects to help ensure that the installation of electrical wiring and devices comply with building codes and safety standards. They are also useful for troubleshooting and maintenance purposes, as they provide a clear reference for identifying and accessing the junction boxes.
What is the purpose of cable layout drawings?
Cable layout drawings serve the purpose of visually illustrating the arrangement of electrical or communication cables in a building or a specific area. They provide valuable information to engineers, contractors, and technicians regarding the cable route, cable type, and cable connections. The drawings help to ensure that the cables are installed correctly and efficiently, minimizing the risk of errors or delays in the installation process. Additionally, cable layout drawings are useful in troubleshooting cable-related issues and making future modifications or upgrades to the system.
How do you calculate cable schedule?
Calculating a cable schedule involves determining the length, size, and type of cable needed for a particular electrical installation. To calculate a cable schedule, the first step is to identify the electrical load requirements of the system and determine the distances between the power source and the various loads. From there, the appropriate cable size and type can be selected based on the current carrying capacity and voltage drop requirements. The cable lengths can then be calculated and recorded in a cable schedule document for reference during installation. It's important to consult with relevant standards and codes as well as qualified professionals in order to ensure a safe and effective electrical installation.










Post a Comment